Negative Feedback
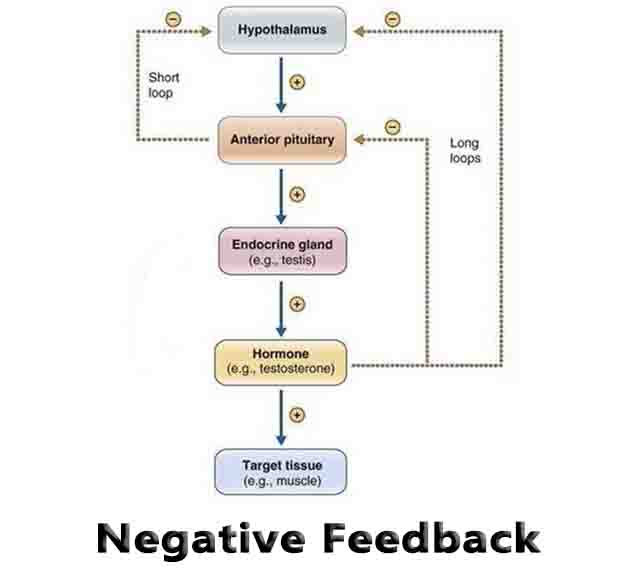
Negative Feedback Definition Negative feedback is a type of regulation in biological systems in which the end product of a process in turn reduces the stimulus of that same process. Feedback, in general, is a regulatory mechanism present in many biological reactions. By allowing certain pathways to be turned off and on, the body can … Read more