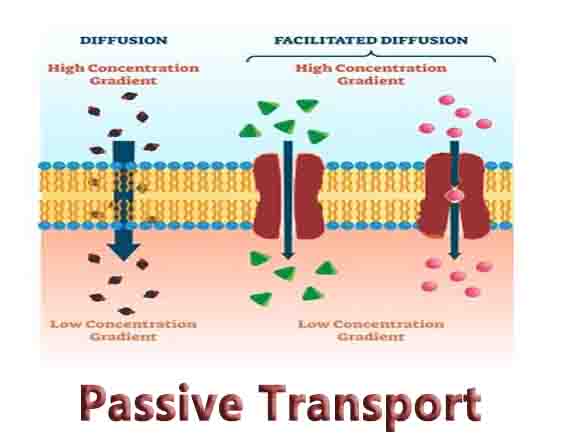
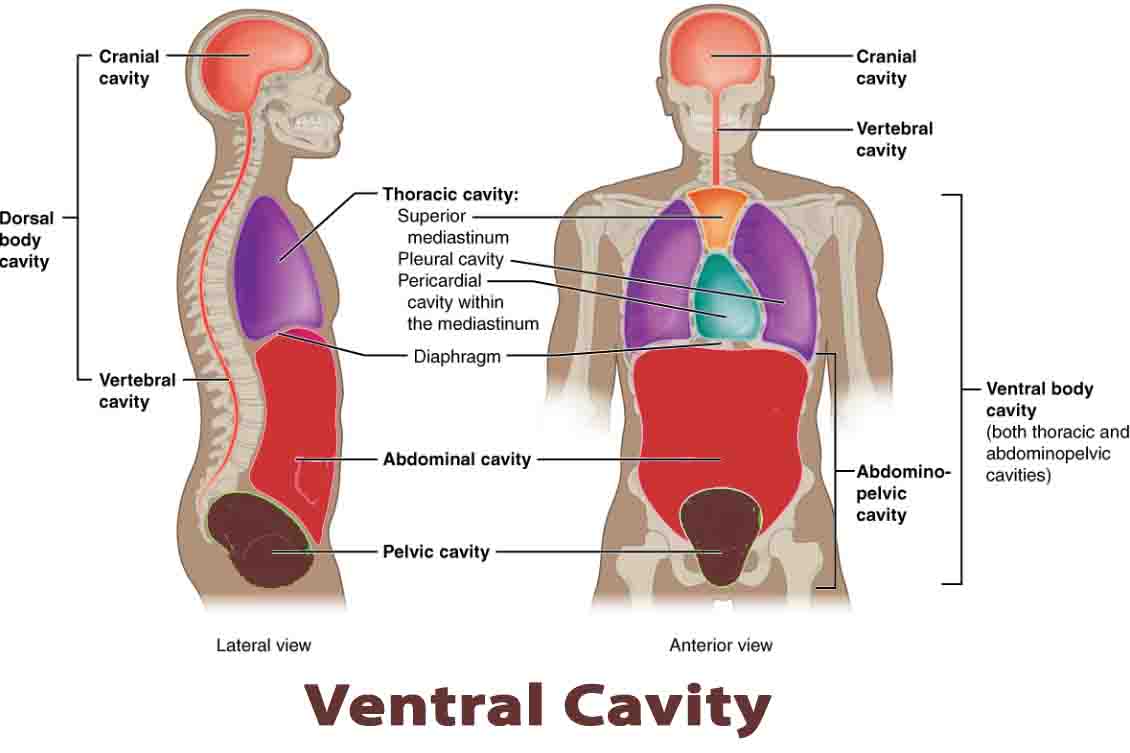
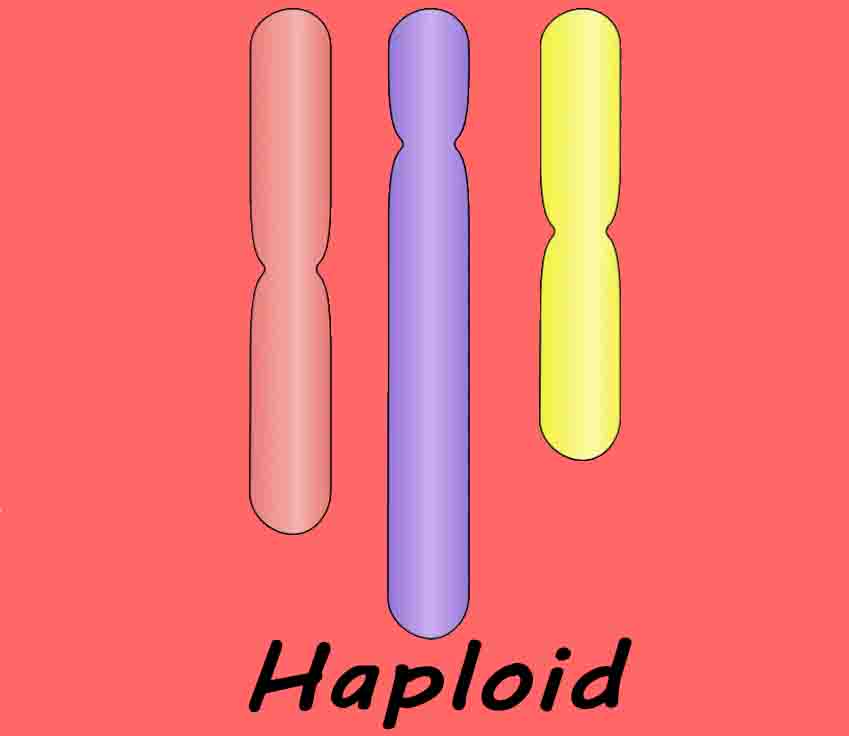
Producer
Producer Definition Producers are organisms capable of creating simple carbohydrates such as glucose, from gaseous carbon dioxide. This process of producing organic molecules from inorganic carbon sources is called primary production. The energy for this process can come from solar radiation, chemical reactions or from the heat in deep ocean geothermal vents. On land, most … Read more